Feb 22, 2024

In the previous Part 1, the basics of API security were discussed. This post elaborates on best practices and provides examples for deeper insights into securing APIs. Explore for essential tips on effectively safeguarding your APIs.
In API interactions, authentication typically uses JSON Web Tokens (JWTs). Users send requests with JWTs to access services. Prioritizing security is crucial, and using robust JWTs is essential. Weak tokens carry significant risks, especially when used across different API services.
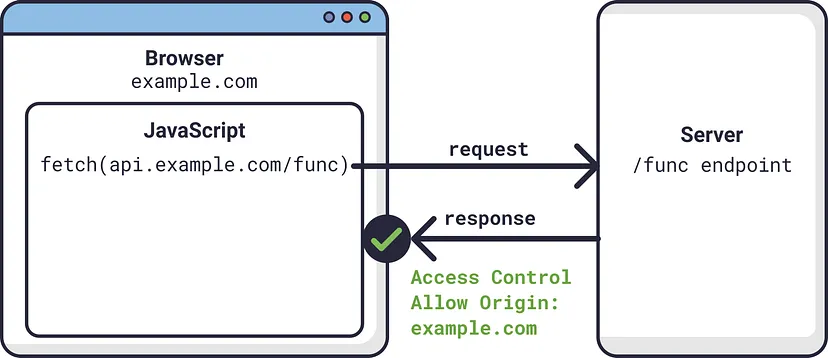
Cross-origin resource sharing is a mechanism that allows restricted resources on a web page to be accessed from another domain outside the domain from which the first resource was served.
The Same-Origin Policy (SOP) is a standard security measure in web browsers. It restricts access to web resources from different origins, accounting for variations in protocol, port, or hostname. While tools like Postman don’t face CORS issues, browsers may encounter problems due to stricter security policies.
Consider the example of “http://example.com/”
from flask_cors import import CORS
CORS(app, allow_origins=["https://example.com", "https://example1.com"])

Implementing rate limiting helps prevent abuse of APIs by restricting the number of requests a user or client can make within a specific timeframe. This ensures fair usage and protects the API from being overwhelmed by excessive traffic, enhancing its reliability and availability for all users.
Implement versioning strategies to ensure backward compatibility during updates. Use versioning to avoid disruptions for existing clients when introducing changes. Consider an API with an endpoint /users in version 1 (/v1/users) returning user data. As you enhance the API, introduce version 2 (/v2/users) with additional fields. Existing clients can continue using /v1/users to ensure their requests aren’t affected by changes, while new clients opt for the improved /v2/users endpoint. This versioning approach allows for a seamless transition and coexistence of different API versions, maintaining consistency and minimizing disruptions during updates.
Implementing robust input validation is crucial for API security. Apply thorough validation checks to ensure each field meets these expected criteria. Validate data types, lengths, and formats to mitigate security risks, preventing potential vulnerabilities related to malformed or malicious JSON input. This proactive validation approach enhances the overall security of your API, providing a safeguard against various attack vectors.
Consider an API that receives a JSON payload for user signup:
Error handling is essential in application development for identifying, diagnosing, and resolving issues, ultimately improving reliability and user experience.
HTTP status codes are utilized by servers to convey the status of a request.
Clear Error Messages: Clear error messages provide user-friendly and informative details about errors, aiding in issue resolution. Instead of a generic “Error 500”, provide a message such as “Please try again later.”
Logging involves recording relevant information about events, errors, or activities in an application. It helps in diagnosing issues and monitoring the application’s behaviour.

Visie
Feb 22, 2024

Visie
Feb 05, 2024

Visie
August 12, 2023

No Credit Card Required
20 free demos per month
© Copyrights 2026 VISIE Limited. All rights reserved.